- 26
- Sep
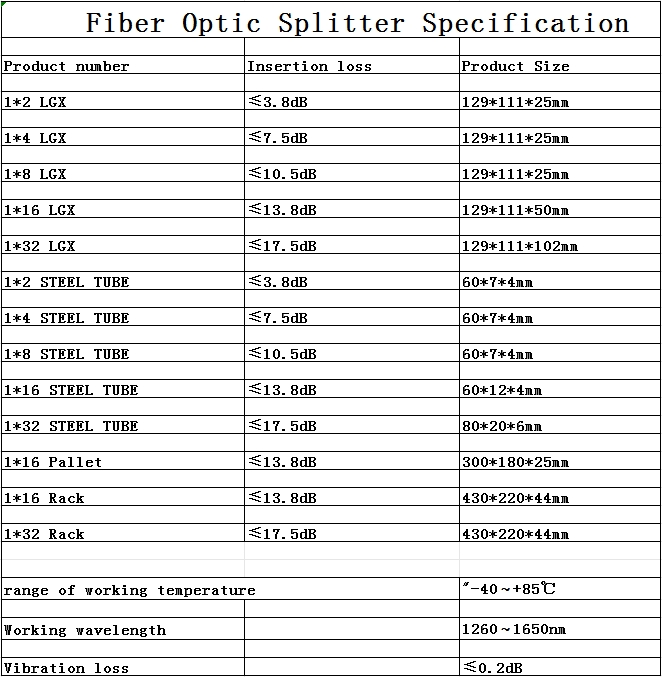
China factory-LinZhu Communication manufacturer supplier of fiber optic splitter LGX PLC Splitter 1*8 sc/apc
Types of PLC splitters
The types of PLC splitters are mainly divided into different packaging methods, including device type, micro package, box package (ABS, LGX), plug-in type, rack type, wall-mounted type, etc.
Device structure
Bare fiber type PLC optical splitter leaves bare fiber at all its ends. Mainly suitable for occasions that are not frequently disassembled, such as cable connector boxes, fiber optic distribution boards, etc.
Micro package structure
Micro optical splitters are packaged in micro steel tubes and can be divided into pigtails with connectors and pigtails without connectors. Connectors usually come in SC, LC, FC and ST types. Can be installed in optical cable connector boxes, module boxes, and wiring boxes.
ABS box type PLC splitter
Box-packaged splitters are currently the most commonly used type by operators. The ABS packaging method is compact and more flexible in application.
LGX type PLC splitter
LGX encapsulates the optical splitter in a small metal box, which can be installed in a 19-inch 1U/2U/3U chassis. The input and output ends have a pigtail structure, which can be easily connected to the ODF panel adapter, saving time. LGX’s compact and micro design is plug-and-play and can be easily installed in optical fiber distribution boxes, ODF sub-frames, optical fiber terminal boxes and optical cable transfer boxes.
Plug-in PLC splitter
The plug-in PLC splitter is installed and fixed in the plug-in box, and the interface types include SC/FC/LC, etc. It is mainly suitable for corridors or outdoor light splitting points under FTTH access mode, and is usually installed in a wall-mounted FTTH box. The commonly used 1X4, 8, 16, 32 and 2X8, 16, 32 PLC splitters are used as plug-in trays for installation in customer-specific enclosures, especially corridor boxes.
Rack Mount PLC Splitter
Rack-mounted optical splitters are designed for standard 19″ cabinet installation, which can meet the requirements for high wiring density in data centers or server rooms. They are generally packaged in metal boxes and are easy to install in fiber optic projects. They are also suitable for PLC splitter devices. Plays a good protective role. There are various adapter installation interfaces such as SC, LC, FC or ST connectors. Rack-mounted optical splitters are widely used in FTTX projects, cable TV systems and data communication centers.
Key parameters of PLC optical splitter
The performance indicators that affect the optical splitter generally include the following:
Insertion Loss(IL)
Insertion loss refers to the reduction of the optical power of the PLC splitter operating wavelength at the specified output port relative to the total input optical power. Simply put, it is the dB loss of each output relative to the input optical power. Generally speaking, the smaller the insertion loss value, the better the splitter performance index.
Return loss
Return loss refers to the number of decibels of the ratio of back-reflected light (scattered light that is continuously transmitted to the input end) to the input light at the fiber connection. The larger the return loss, the better, in order to reduce the impact of reflected light on the light source and system. Influence.
Directionality
Directivity refers to the ratio of the output optical power at the non-injected light end on the same side to the injected optical power (measured wavelength) when the PLC splitter is operating normally.
Polarization dependent loss
Polarization-dependent loss refers to the maximum change in the output optical power of each output port of the PLC splitter when the polarization state of the transmitted optical signal changes in all polarization states.
Isolation
Isolation refers to the ability of a certain optical path of a fiber optic splitter to isolate optical signals from other optical paths.
PLC optical splitter is used in FTTR, FTTX, PON networks
The PON system can implement FTTx and use optical fiber access to provide solutions for the “last mile” of the access network. A typical PON system consists of optical line terminal (OLT), optical distribution network (ODN), optical network unit/optical network terminal
The optical splitter is the most important optical passive component in ODN equipment. In FTTx, the optical splitter allows multiple users to share a PON interface. The optical splitting construction of the PON network includes primary splitting and secondary splitting. First-level optical splitting has the characteristics of high flexibility and low operating costs, and is mainly used in urban areas where users are concentrated. Second-level splitting has low initial investment and can be used in areas where users are dispersed. There are two principles for spectroscopic setting: one is to use one-level split cylinder as much as possible, and the other is to use no more than two spectroscopic levels.
The first-level method means that the optical splitter is distributed in the optical fiber distribution box, a single optical fiber is directly connected to the central office OLT, and the other end is connected to multiple ONT fibers at the user end through multiple optical fibers. The first-level splitter can only be connected to one splitter. Generally, a splitter with a larger number of splitters is used, such as 1:32 or 1:64. For secondary light splitting, a 1:8 or 1:16 splitter is generally used at the primary light splitting point, and a 1:4 or 1:8 splitter is used at the secondary light splitting point.
